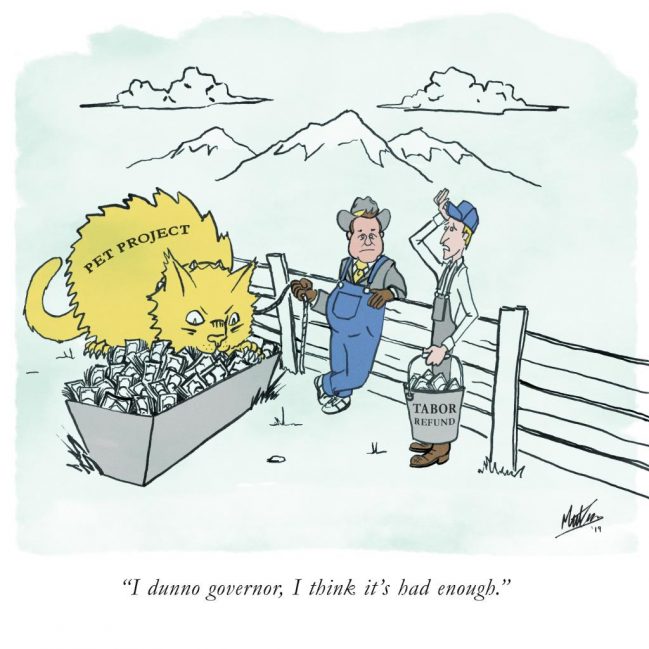
Amend TABOR to include ‘fees’
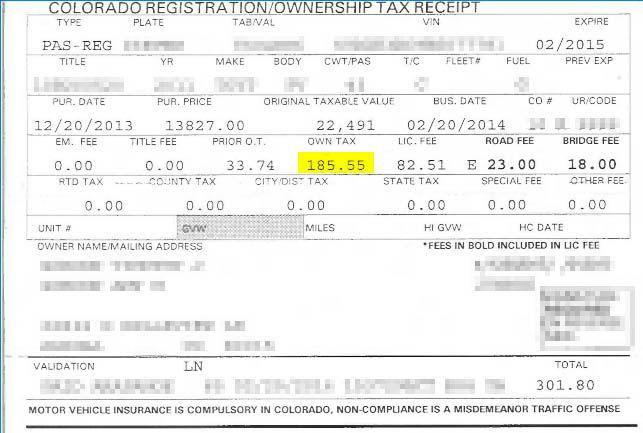
Just received my annual registration for my 2004 Subaru Outback and just reading the receipt my blood again begins to boil. The only “tax” listed is $3 for specific ownership tax, the next 12 items are all “fees”. Age of vehicle fee $7, bridge safety surcharge fee $23, clerk hire fee $4, county road and bridge fee $1.50, emergency medical services fee $2, emissions-statewide air account fee, $0.5 and many more, for a grand total of $70.17.
These are in addition to all of the gas taxes we all pay each time we fill up. I don’t mind being charged for normal needs-based surcharges such as those required to maintain our infrastructure but lets call it what they are.. Taxes! Since I/we are already paying all of these “fees” to the state, it’s another reason why I am appalled at the thought of eventually having to also pay more and more for the myriad of oncoming toll lanes throughout the state.