In celebration of thirty years of the Colorado Taxpayer’s Bill of Rights (TABOR), ALEC today launched its Fiscal Rules campaign, featuring the interactive Fiscal Rules microsite, new Fiscal Rules animated video, and new report, “TABOR Turns 30: Thirty Years of Colorado’s Taxpayer’s Bill of Rights.”
Category Archives: Colorado Legislature
Did You Know This About TABOR?
#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw

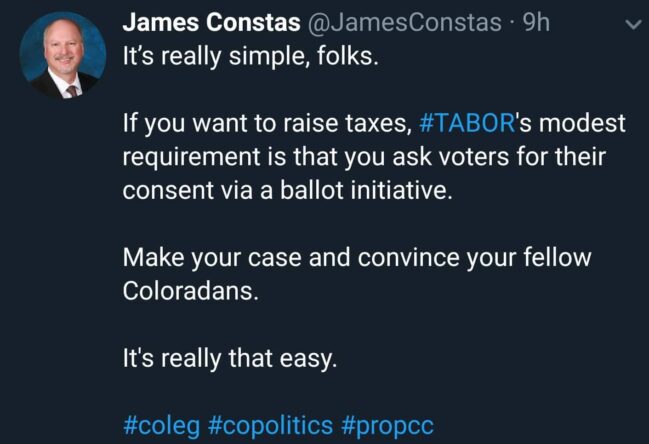
With TABOR, Make Your Case And Convince Your Fellow Coloradans
#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw
Maybe it’s time to call off one-party rule in Colorado
October 28, 2022
Maybe it’s time to call off one-party rule in Colorado
By C.S. Boddie
Colorado has been under one-party rule by the Democrats for two or three elections now. It’s a mess. One of the people who helped create the mess, state senator Brittany Pettersen, is now running for Congress against Republican Erik Aadland in Colorado’s redrawn CD7. Voters are making their choice right now.
Will Coloradoans elect Pettersen to a higher office? Seems as though it would be failing her upward as Democrats did with Biden, and we see how that turned out.
During the recent 9News Debate, where journalists tossed softballs at Pettersen, the Democrat was first described in a voiceover as a Democratic state senator Brittany Pettersen who has focused on support for working families, mental health care and substance abuse issues.
Let’s focus on the phrase “working families” here. Has Pettersen really supported them? We can check her words for clues.
Pettersen’s website reads, “As a Colorado legislator, I passed the nation’s strongest Equal Pay for Equal Work Act, Colorado’s Red Flag law, and the Secure Savings Act.” The first one seems supportive of working people, but it’s also a liberal darling. The other two do not seem to relate; whether or not those accomplishments benefited working families is questionable.
Inflation is the top concern of working families; they are being harmed by record inflation in Colorado every day. What has Pettersen said about inflation? The word “inflation” does not appear anywhere on the candidate’s website. However, the website is chock-full of Democrat canned phrases and talking points, which echo Governor Polis and President Biden.
Pettersen claims that as a state senator, she ensured that every Colorado taxpayer received a $750 check in July to provide relief in this difficult time (still referring to the pandemic). The truth is that citizens received a refund because of the Taxpayer Bill of Rights (TABOR), not because of Pettersen. Democrats just made the payment happen earlier so that it could be used as a talking point for the election.
The website does include another bit about rising prices without mentioning the word “inflation”: “Prices for everything are going up because big corporations are increasing costs in a time of crisis while they are making record profits, and politicians in Washington aren’t putting our families first. In the Colorado Senate, Brittany sponsored legislation to hold companies accountable for price gouging and will do the same in Congress.”
Nothing about how Democrats spending like drunken sailors has caused record inflation. Nothing about how the Democrats’ war on oil and gas has raised prices on everything. Oh, but she cut the gas tax in Colorado.
Pettersen’s website says, “In Congress, Brittany will fight to help address critical workforce needs by passing loan forgiveness programs in areas like education and health care.” How does that address inflation?
How can a candidate help working families in Congress if she does not even recognize what a problem inflation is for them or admit that the source of inflation is government spending?
On taxes, Pettersen’s website repeats another old, false Democrat chestnut: “She will fight to repeal the 2017 Trump tax cuts that only benefited the wealthy and largest corporations, and will work to help give breaks to the middle class who have been left holding the bag for far too long.” Seems like every candidate needs to get Trump’s name out there somehow.
What about crime? Crime is another great concern of working families in Colorado. How can they get to work on time if their car is stolen? Car thefts have greatly increased while Pettersen has been in the state Senate. Any ideas?
Nope. No mention of crime and what she will do to reduce crime. But she does mention protecting democracy.
How can Pettersen bring answers to one of the biggest concerns of our state’s working families when she doesn’t even mention crime as she is running to be their next representative in Congress? And, by the way, the USA is representative democracy or a constitutional republic, not a direct democracy; shouldn’t a candidate who wants to represent people in Congress know that and not just parrot the talking points of her party’s elite?
By focusing only on the phrase “working families,” one can see a picture emerging of who Brittany Pettersen will be in Congress, and the picture is not a good one. She may be another Squad member. She will likely be only a rubber stamp for Democrats’ harmful policies that do not help, that do harm, working families all across the USA.
As for mental health and substance abuse issues, well, Pettersen cosponsored a bill to create heroin safe injection sites, but it did not go to a vote. She sponsored a useless bill to fix flawed fentanyl law. Enough said.
Let’s not fail Brittany Pettersen up into a seat in Congress.
C.S. Boddie writes for Meadowlark Press.

TABOR Foundation board member Natalie Menten on her opposition to Prop 123
How To Vote On Local TABOR ballot issues

The column above provides how-to and then links to this website which has the local TABOR ballot issue list:

“We The People” Is TABOR
#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw

Colorado & Taxes

#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw
Even key Dems dis Prop. 123; vote NO
#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw
Even key Dems dis Prop. 123; vote NO
- By Ben Murrey
- Oct 12, 2022Updated Oct 12, 2022

Ben Murrey
Thanks to the Taxpayer’s Bill of Rights, commonly known as “TABOR,” Coloradans will receive nearly $4 billion in excess revenue refunded from the state this year. That’s where those $750 checks for individuals and $1,500 for couples came from over the summer. On the ballot this year, Proposition 123 is asking voters to give up their refunds, at least in part.
If adopted by voters, the measure would reduce TABOR refunds by about $86 per person, based on information from the state voter booklet or “Blue Book.”
The measure dedicates up to 0.1% of income tax revenue to affordable housing programs administered by state bureaucracies. For years in which the state has a TABOR surplus, that would reduce TABOR refunds by about $300 million. State economists currently project refunds for at least the next three years.
Even Democrats — who rarely refuse the opportunity to spend more of your money on new government programs — have been skeptical of the measure.
Democratic state Sen. Chris Hansen, of Denver, expressed concern that Proposition 123 could eat directly into the state’s ability to spend on other priorities.
“There’s no free lunch,” Hansen said referencing the measure. “K-12 and higher education (is) where the marginal dollar is in our state budget. So $1 less means $1 less for education.”
The statement proves a bit disingenuous, but the senator is right to say there is no such thing as a free lunch. Continue reading
I Will Resist You If….

#DontBeFooled
#ItsYourMoneyNotTheirs
#VoteOnTaxesAndFees
#FeesAreTaxes
#TABOR
#ThankGodForTABOR
#FollowTheMoney
#FollowTheLaw
